SSD網絡tensorflow版本源碼深入分析
以VGG-16作爲特徵提取層實現SSD網絡的代碼,解讀SSD網絡代碼實現的各個細節,從輸入參數、默認框的位置匹配、寬高比率、放縮比率、各層默認框的生成、到損失函數計算、整個SSD網絡框架代碼實現都一一解讀。
一:SSD網絡相關參數代碼解析
源代碼中對SSD網絡需要的6個層大小,默認框大小、最小與最大放縮比率、默認框不同寬高比、步長感受野、並交比等參數給出了相關默認值。代碼如下:
img_shape=(300, 300),
num_classes=21,
no_annotation_label=21,
feat_layers=['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11'],
feat_shapes=[(38, 38), (19, 19), (10, 10), (5, 5), (3, 3), (1, 1)],
anchor_size_bounds=[0.15, 0.90],
# anchor_size_bounds=[0.20, 0.90],
anchor_sizes=[(21., 45.),
(45., 99.), # 0.18
(99., 153.),
(153., 207.),
(207., 261.),
(261., 315.)],
# anchor_sizes=[(30., 60.),
# (60., 111.),
# (111., 162.),
# (162., 213.),
# (213., 264.),
# (264., 315.)],
anchor_ratios=[[2, .5],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5],
[2, .5]],
anchor_steps=[8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300],
anchor_offset=0.5,
normalizations=[20, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1],
prior_scaling=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2]img_shape表示輸入圖像大小爲300x300大小
num_classes 表示識別種類是21種
feat_layers表示特徵提取使用VGG-16卷積層的4、7、8、9、10、11層
feat_shape表示各個層寬高大小
anchor_sizes表示各個層對於的默認框的寬與高
anchor_ratios表示支持的寬高比例,SSD論文支持的寬高比例[1,2,3,1/2,1/3]具體到各個層可以選擇的。
Anchor_steps表示的每個grid的大小,或者是感受野的大小,grid越小的感受野越大,對應只能檢測更大的對象,比如最後卷積層11層,只能檢測比較大的對象。這個在SSD算法作者的論文有一張圖可以說明這個問題: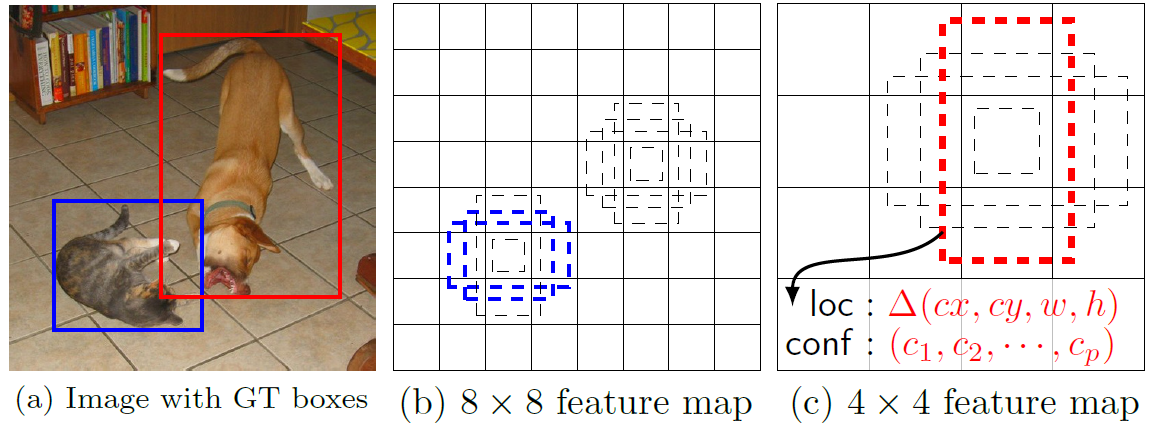
圖-1
圖a表示輸入圖像,有兩個正確標註框、b表示在grid是8x8的cell上,在每個cell有5個不同比率的默認框,最終計算並交比率,表示藍色框大於0.5(就是參數anchor_offset=0.5),成功匹配,而對狗在grid是8x8的上面無法匹配,在它的下一層4x4grid上面成功匹配-紅色的框。
二:生成各層的默認框與中心位置
方法ssd_anchors_all_layers生成所有層所有的默認框,代碼實現如下:
def ssd_anchors_all_layers(img_shape,
layers_shape,
anchor_sizes,
anchor_ratios,
anchor_steps,
offset=0.5,
dtype=np.float32):
"""Compute anchor boxes for all feature layers.
"""
layers_anchors = []
for i, s in enumerate(layers_shape):
anchor_bboxes = ssd_anchor_one_layer(img_shape, s,
anchor_sizes[i],
anchor_ratios[i],
anchor_steps[i],
offset=offset, dtype=dtype)
layers_anchors.append(anchor_bboxes)
return layers_anchorsssd_anchor_one_layer方法實現了生成每一層的默認框,代碼如下:
def ssd_anchor_one_layer(img_shape,
feat_shape,
sizes,
ratios,
step,
offset=0.5,
dtype=np.float32):
"""Computer SSD default anchor boxes for one feature layer.
Determine the relative position grid of the centers, and the relative
width and height.
Arguments:
feat_shape: Feature shape, used for computing relative position grids;
size: Absolute reference sizes;
ratios: Ratios to use on these features;
img_shape: Image shape, used for computing height, width relatively to the
former;
offset: Grid offset.
Return:
y, x, h, w: Relative x and y grids, and height and width.
"""
# Compute the position grid: simple way.
# y, x = np.mgrid[0:feat_shape[0], 0:feat_shape[1]]
# y = (y.astype(dtype) + offset) / feat_shape[0]
# x = (x.astype(dtype) + offset) / feat_shape[1]
# Weird SSD-Caffe computation using steps values...
y, x = np.mgrid[0:feat_shape[0], 0:feat_shape[1]]
y = (y.astype(dtype) + offset) * step / img_shape[0]
x = (x.astype(dtype) + offset) * step / img_shape[1]
# Expand dims to support easy broadcasting.
y = np.expand_dims(y, axis=-1)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=-1)
# Compute relative height and width.
# Tries to follow the original implementation of SSD for the order.
# 默認支持+支持的寬高比率,得到該層總的支持boxes數目
num_anchors = len(sizes) + len(ratios)
h = np.zeros((num_anchors, ), dtype=dtype)
w = np.zeros((num_anchors, ), dtype=dtype)
# Add first anchor boxes with ratio=1.
h[0] = sizes[0] / img_shape[0]
w[0] = sizes[0] / img_shape[1]
di = 1
# 默認支持的default boxes
if len(sizes) > 1:
h[1] = math.sqrt(sizes[0] * sizes[1]) / img_shape[0]
w[1] = math.sqrt(sizes[0] * sizes[1]) / img_shape[1]
di += 1
# 通過比率支持的anchor boxes
for i, r in enumerate(ratios):
h[i+di] = sizes[0] / img_shape[0] / math.sqrt(r)
w[i+di] = sizes[0] / img_shape[1] * math.sqrt(r)
# 返回該層總的anchor boxes數目(每個boxes的中心位置(y, x), 高度h與寬度x)
return y, x, h, w對源代碼我已經做了中文註解、方便大家閱讀,其實這裏大家最重要的是要明白計算中心位置是使用原著論文中計算default box的中心位置的公式,其次就是生成default box。
三:預測與損失函數
對於每個default box如果最終的並交比超過0.5以上的進行匹配預測會生成(C+4)個值,其中C就是各個種類的得分向量,多少與種類num_classes相同、另外4個值位置信息,這裏不會預測box的中心位置與寬高,而是預測它們的offset或者delta。可以參看圖-1。最終計算的損失分爲兩個部分,分別是位置信息損失與預測種類損失。對於grid是MXN大小的卷積層來說,假設有K個default box,最終輸出的預測數據爲(C+4)kM*N。多個box預測層的代碼實現如下:
def ssd_multibox_layer(inputs,
num_classes,
sizes,
ratios=[1],
normalization=-1,
bn_normalization=False):
"""Construct a multibox layer, return a class and localization predictions.
"""
net = inputs
if normalization > 0:
net = custom_layers.l2_normalization(net, scaling=True)
# Number of anchors.
num_anchors = len(sizes) + len(ratios)
# Location.
num_loc_pred = num_anchors * 4
loc_pred = slim.conv2d(net, num_loc_pred, [3, 3], activation_fn=None,
scope='conv_loc')
loc_pred = custom_layers.channel_to_last(loc_pred)
loc_pred = tf.reshape(loc_pred,
tensor_shape(loc_pred, 4)[:-1]+[num_anchors, 4])
# Class prediction.
num_cls_pred = num_anchors * num_classes
cls_pred = slim.conv2d(net, num_cls_pred, [3, 3], activation_fn=None,
scope='conv_cls')
cls_pred = custom_layers.channel_to_last(cls_pred)
cls_pred = tf.reshape(cls_pred,
tensor_shape(cls_pred, 4)[:-1]+[num_anchors, num_classes])
return cls_pred, loc_pred損失計算的代碼如下:
def ssd_losses(logits, localisations,
gclasses, glocalisations, gscores,
match_threshold=0.5,
negative_ratio=3.,
alpha=1.,
label_smoothing=0.,
device='/cpu:0',
scope=None):
with tf.name_scope(scope, 'ssd_losses'):
lshape = tfe.get_shape(logits[0], 5)
num_classes = lshape[-1]
batch_size = lshape[0]
# Flatten out all vectors!
flogits = []
fgclasses = []
fgscores = []
flocalisations = []
fglocalisations = []
for i in range(len(logits)):
flogits.append(tf.reshape(logits[i], [-1, num_classes]))
fgclasses.append(tf.reshape(gclasses[i], [-1]))
fgscores.append(tf.reshape(gscores[i], [-1]))
flocalisations.append(tf.reshape(localisations[i], [-1, 4]))
fglocalisations.append(tf.reshape(glocalisations[i], [-1, 4]))
# And concat the crap!
logits = tf.concat(flogits, axis=0)
gclasses = tf.concat(fgclasses, axis=0)
gscores = tf.concat(fgscores, axis=0)
localisations = tf.concat(flocalisations, axis=0)
glocalisations = tf.concat(fglocalisations, axis=0)
dtype = logits.dtype
# Compute positive matching mask...
pmask = gscores > match_threshold
fpmask = tf.cast(pmask, dtype)
n_positives = tf.reduce_sum(fpmask)
# Hard negative mining...
no_classes = tf.cast(pmask, tf.int32)
predictions = slim.softmax(logits)
nmask = tf.logical_and(tf.logical_not(pmask),
gscores > -0.5)
fnmask = tf.cast(nmask, dtype)
nvalues = tf.where(nmask,
predictions[:, 0],
1. - fnmask)
nvalues_flat = tf.reshape(nvalues, [-1])
# Number of negative entries to select.
max_neg_entries = tf.cast(tf.reduce_sum(fnmask), tf.int32)
n_neg = tf.cast(negative_ratio * n_positives, tf.int32) + batch_size
n_neg = tf.minimum(n_neg, max_neg_entries)
val, idxes = tf.nn.top_k(-nvalues_flat, k=n_neg)
max_hard_pred = -val[-1]
# Final negative mask.
nmask = tf.logical_and(nmask, nvalues < max_hard_pred)
fnmask = tf.cast(nmask, dtype)
# Add cross-entropy loss.
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy_pos'):
loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,
labels=gclasses)
loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * fpmask), batch_size, name='value')
tf.losses.add_loss(loss)
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy_neg'):
loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,
labels=no_classes)
loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * fnmask), batch_size, name='value')
tf.losses.add_loss(loss)
# Add localization loss: smooth L1, L2, ...
with tf.name_scope('localization'):
# Weights Tensor: positive mask + random negative.
weights = tf.expand_dims(alpha * fpmask, axis=-1)
loss = custom_layers.abs_smooth(localisations - glocalisations)
loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * weights), batch_size, name='value')
tf.losses.add_loss(loss)最終的SSD網絡構建代碼,默認是基於VGG-16,輸入圖像大小爲300x300。其符合原著SSD論文中作者給出的SSD網絡模型圖:
代碼如下:
def ssd_net(inputs,
num_classes=SSDNet.default_params.num_classes,
feat_layers=SSDNet.default_params.feat_layers,
anchor_sizes=SSDNet.default_params.anchor_sizes,
anchor_ratios=SSDNet.default_params.anchor_ratios,
normalizations=SSDNet.default_params.normalizations,
is_training=True,
dropout_keep_prob=0.5,
prediction_fn=slim.softmax,
reuse=None,
scope='ssd_300_vgg'):
"""SSD net definition.
"""
# if data_format == 'NCHW':
# inputs = tf.transpose(inputs, perm=(0, 3, 1, 2))
# End_points collect relevant activations for external use.
end_points = {}
with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'ssd_300_vgg', [inputs], reuse=reuse):
# Original VGG-16 blocks.
net = slim.repeat(inputs, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv1')
end_points['block1'] = net
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool1')
# Block 2.
net = slim.repeat(net, 2, slim.conv2d, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2')
end_points['block2'] = net
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool2')
# Block 3.
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3')
end_points['block3'] = net
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool3')
# Block 4.
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4')
end_points['block4'] = net
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool4')
# Block 5.
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5')
end_points['block5'] = net
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=1, scope='pool5')
# Additional SSD blocks.
# Block 6: let's dilate the hell out of it!
net = slim.conv2d(net, 1024, [3, 3], rate=6, scope='conv6')
end_points['block6'] = net
net = tf.layers.dropout(net, rate=dropout_keep_prob, training=is_training)
# Block 7: 1x1 conv. Because the fuck.
net = slim.conv2d(net, 1024, [1, 1], scope='conv7')
end_points['block7'] = net
net = tf.layers.dropout(net, rate=dropout_keep_prob, training=is_training)
# Block 8/9/10/11: 1x1 and 3x3 convolutions stride 2 (except lasts).
end_point = 'block8'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = custom_layers.pad2d(net, pad=(1, 1))
net = slim.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')
end_points[end_point] = net
end_point = 'block9'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = custom_layers.pad2d(net, pad=(1, 1))
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')
end_points[end_point] = net
end_point = 'block10'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')
end_points[end_point] = net
end_point = 'block11'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')
end_points[end_point] = net
# Prediction and localisations layers.
predictions = []
logits = []
localisations = []
for i, layer in enumerate(feat_layers):
with tf.variable_scope(layer + '_box'):
p, l = ssd_multibox_layer(end_points[layer],
num_classes,
anchor_sizes[i],
anchor_ratios[i],
normalizations[i])
predictions.append(prediction_fn(p))
logits.append(p)
localisations.append(l)
return predictions, localisations, logits, end_points
ssd_net.default_image_size = 300tensorflow相關視頻教程
tensorflow基礎入門
tensorflow object detection API對象檢測教程

