Python基礎(二)
Python 運算符(算術運算、比較運算、賦值運算、邏輯運算、成員運算)
基本數據類型(數字、布爾值、字符串、列表、元組、字典、set集合)
for 循環
enumrate
range和xrange
編碼與進制轉換
Python 運算符
1、算術運算:
2、比較運算:
3、賦值運算:
4、邏輯運算:
5、成員運算:
基本數據類型
1、數字
int(整型)
在32位機器上,整數的位數爲32位,取值範圍爲-2**31~2**31-1,即-2147483648~2147483647
在64位系統上,整數的位數爲64位,取值範圍爲-2**63~2**63-1,即-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807
#返回表示該數字的時佔用的最少位數
>>> (951).bit_length()
10
#返回絕對值
>>> (95).__abs__()
95
>>> (-95).__abs__()
95
#用來區分數字和字符串的
>>> (95).__add__(1)
96
>>> (95).__add__("1")
NotImplemented
#判斷一個整數對象是否爲0,如果爲0,則返回False,如果不爲0,則返回True
>>> (95).__bool__()
True
>>> (0).__bool__()
False
#判斷兩個值是否相等
>>> (95).__eq__(95)
True
>>> (95).__eq__(9)
False
#判斷是否不等於
>>> (95).__ne__(9)
True
>>> (95).__ne__(95)
False
#判斷是否大於等於
>>> (95).__ge__(9)
True
>>> (95).__ge__(99)
False
#判斷是否大於
>>> (95).__gt__(9)
True
>>> (95).__gt__(99)
False
#判斷是否小於等於
>>> (95).__le__(99)
True
>>> (95).__le__(9)
False
#判斷是否小於
>>> (95).__lt__(9)
False
>>> (95).__lt__(99)
True
#加法運算
>>> (95).__add__(5)
100
#減法運算
>>> (95).__sub__(5)
90
#乘法運算
>>> (95).__mul__(10)
950
#除法運算
>>> (95).__truediv__(5)
19.0
#取模運算
>>> (95).__mod__(9)
5
#冪運算
>>> (2).__pow__(10)
1024
#整除,保留結果的整數部分
>>> (95).__floordiv__(9)
>>>
#轉換爲整型
>>> (9.5).__int__()
9
#返回一個對象的整數部分
>>> (9.5).__trunc__()
9
#將正數變爲負數,將負數變爲正數
>>> (95).__neg__()
-95
>>> (-95).__neg__()
95
#將一個正數轉爲字符串
>>> a = 95
>>> a = a.__str__()
>>> print(type(a))
<class 'str'>
#將一個整數轉換成浮點型
>>> (95).__float__()
95.0
#轉換對象的類型
>>> (95).__format__('f')
'95.000000'
>>> (95).__format__('b')
'1011111'
#在內存中佔多少個字節
>>> a = 95
>>> a.__sizeof__()
28class int(object):
"""
int(x=0) -> integer
int(x, base=10) -> integer
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point
numbers, this truncates towards zero.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string,
bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the
given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded
by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36.
Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
"""
def bit_length(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
int.bit_length() -> int
Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary.
"""
"""
表示該數字返回時佔用的最少位數
>>> (951).bit_length()
"""
return 0
def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int."""
"""
返回該複數的共軛複數
#返回複數的共軛複數
>>> (95 + 11j).conjugate()
(95-11j)
#返回複數的實數部分
>>> (95 + 11j).real
95.0
#返回複數的虛數部分
>>> (95 + 11j).imag
11.0
"""
pass
@classmethod # known case
def from_bytes(cls, bytes, byteorder, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown; NOTE: unreliably restored from __doc__
"""
int.from_bytes(bytes, byteorder, *, signed=False) -> int
Return the integer represented by the given array of bytes.
The bytes argument must be a bytes-like object (e.g. bytes or bytearray).
The byteorder argument determines the byte order used to represent the
integer. If byteorder is 'big', the most significant byte is at the
beginning of the byte array. If byteorder is 'little', the most
significant byte is at the end of the byte array. To request the native
byte order of the host system, use `sys.byteorder' as the byte order value.
The signed keyword-only argument indicates whether two's complement is
used to represent the integer.
"""
"""
這個方法是在Python3.2的時候加入的,python官方給出了下面幾個例子:
>>> int.from_bytes(b'\x00\x10', byteorder='big')
>>> int.from_bytes(b'\x00\x10', byteorder='little')
>>> int.from_bytes(b'\xfc\x00', byteorder='big', signed=True)
-1024
>>> int.from_bytes(b'\xfc\x00', byteorder='big', signed=False)
>>> int.from_bytes([255, 0, 0], byteorder='big')
"""
pass
def to_bytes(self, length, byteorder, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown; NOTE: unreliably restored from __doc__
"""
int.to_bytes(length, byteorder, *, signed=False) -> bytes
Return an array of bytes representing an integer.
The integer is represented using length bytes. An OverflowError is
raised if the integer is not representable with the given number of
bytes.
The byteorder argument determines the byte order used to represent the
integer. If byteorder is 'big', the most significant byte is at the
beginning of the byte array. If byteorder is 'little', the most
significant byte is at the end of the byte array. To request the native
byte order of the host system, use `sys.byteorder' as the byte order value.
The signed keyword-only argument determines whether two's complement is
used to represent the integer. If signed is False and a negative integer
is given, an OverflowError is raised.
"""
"""
python官方給出了下面幾個例子:
>>> (1024).to_bytes(2, byteorder='big')
b'\x04\x00'
>>> (1024).to_bytes(10, byteorder='big')
b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x04\x00'
>>> (-1024).to_bytes(10, byteorder='big', signed=True)
b'\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xfc\x00'
>>> x = 1000
>>> x.to_bytes((x.bit_length() // 8) + 1, byteorder='little')
b'\xe8\x03'
"""
pass
def __abs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" abs(self)"""
"""
返回一個絕對值
>>> (95).__abs__()
-95
>>> (-95).__abs__()
"""
pass
def __add__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self+value."""
"""
加法,也可區分數字和字符串
>>> (95).__add__(1)
>>> (95).__add__("1")
NotImplemented
>>>
"""
pass
def __and__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self&value."""
pass
def __bool__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" self != 0 """
"""
判斷一個整數對象是否爲0,如果爲0,則返回False,如果不爲0,則返回True
>>> (95).__bool__()
True
>>> (0).__bool__()
False
"""
pass
def __ceil__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Ceiling of an Integral returns itself. """
pass
def __divmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return divmod(self, value). """
"""
返回一個元組,第一個元素爲商,第二個元素爲餘數
>>> (9).__divmod__(5)
(1, 4)
"""
pass
def __eq__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self==value. """
"""
判斷兩個值是否相等
>>> (95).__eq__(95)
True
>>> (95).__eq__(9)
False
"""
pass
def __float__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" float(self) """
"""
將一個整數轉換成浮點型
>>> (95).__float__()
95.0
"""
pass
def __floordiv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self//value. """
"""
整除,保留結果的整數部分
>>> (95).__floordiv__(9)
"""
pass
def __floor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Flooring an Integral returns itself. """
"""
返回本身
>>> (95).__floor__()
"""
pass
def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
轉換對象的類型
>>> (95).__format__('f')
'95.000000'
>>> (95).__format__('b')
'1011111'
"""
pass
def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return getattr(self, name). """
"""
判斷這個類中是否包含這個屬性,如果包含則打印出值,如果不包含,就報錯了
>>> (95).__getattribute__('__abs__')
<method-wrapper '__abs__' of int object at 0x9f93c0>
>>> (95).__getattribute__('__aaa__')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'int' object has no attribute '__aaa__'
"""
pass
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __ge__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>=value. """
"""
判斷是否大於等於
>>> (95).__ge__(9)
True
>>> (95).__ge__(99)
False
"""
pass
def __gt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>value. """
"""
判斷是否大於
>>> (95).__gt__(9)
True
>>> (95).__gt__(99)
False
"""
pass
def __hash__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return hash(self). """
"""
計算哈希值,整數返回本身
>>> (95).__hash__()
>>> (95.95).__hash__()
"""
pass
def __index__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self converted to an integer, if self is suitable for use as an index into a list. """
pass
def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__
"""
這個是一個類的初始化方法,當int類被實例化的時候,這個方法默認就會被執行
"""
"""
int(x=0) -> integer
int(x, base=10) -> integer
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point
numbers, this truncates towards zero.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string,
bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the
given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded
by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36.
Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __int__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" int(self) """
"""
轉換爲整型
>>> (9.5).__int__()
"""
pass
def __invert__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" ~self """
pass
def __le__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<=value. """
"""
判斷是否小於等於
>>> (95).__le__(99)
True
>>> (95).__le__(9)
False
"""
pass
def __lshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<<value. """
"""
用於二進制位移,這個是向左移動
>>> bin(95)
'0b1011111'
>>> a = (95).__lshift__(2)
>>> bin(a)
'0b101111100'
>>>
"""
pass
def __lt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<value. """
"""
判斷是否小於
>>> (95).__lt__(9)
False
>>> (95).__lt__(99)
True
"""
pass
def __mod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self%value. """
"""
取模 %
>>> (95).__mod__(9)
"""
pass
def __mul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self*value. """
"""
乘法 *
>>> (95).__mul__(10)
"""
pass
def __neg__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" -self """
"""
將正數變爲負數,將負數變爲正數
>>> (95).__neg__()
-95
>>> (-95).__neg__()
"""
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """
pass
def __ne__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self!=value. """
"""
不等於
>>> (95).__ne__(9)
True
>>> (95).__ne__(95)
False
"""
pass
def __or__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self|value. """
"""
二進制或的關係,只要有一個爲真,就爲真
>>> a = 4
>>> b = 0
>>> a.__or__(b) # a --> 00000100 b --> 00000000
>>> b = 1 # b --> 00000001
>>> a.__or__(b)
"""
pass
def __pos__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" +self """
pass
def __pow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return pow(self, value, mod). """
"""
冪
>>> (2).__pow__(10)
"""
pass
def __radd__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signatre unknown
""" Return value+self. """
"""
加法,將value放在前面
>>> a.__radd__(b) # 相當於 b+a
"""
pass
def __rand__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value&self. """
"""
二進制與的關係,兩個都爲真,才爲真,有一個爲假,就爲假
"""
pass
def __rdivmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return divmod(value, self). """
pass
def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return repr(self). """
pass
def __rfloordiv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value//self. """
pass
def __rlshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value<<self. """
pass
def __rmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value%self. """
pass
def __rmul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value*self. """
pass
def __ror__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value|self. """
pass
def __round__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Rounding an Integral returns itself.
Rounding with an ndigits argument also returns an integer.
"""
pass
def __rpow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return pow(value, self, mod). """
pass
def __rrshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value>>self. """
pass
def __rshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>>value. """
pass
def __rsub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value-self. """
pass
def __rtruediv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value/self. """
pass
def __rxor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value^self. """
pass
def __sizeof__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Returns size in memory, in bytes """
"""
在內存中佔多少個字節
>>> a = 95
>>> a.__sizeof__()
"""
pass
def __str__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return str(self). """
"""
將一個正數轉爲字符串
>>> a = 95
>>> a = a.__str__()
>>> print(type(a))
<class 'str'>
"""
pass
def __sub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self-value. """
"""
減法運算
>>> (95).__sub__(5)
"""
pass
def __truediv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self/value. """
"""
除法運算
>>> (95).__truediv__(5)
19.0
"""
pass
def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Truncating an Integral returns itself. """
"""
返回一個對象的整數部分
>>> (95.95).__trunc__()
"""
pass
def __xor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self^value. """
"""
將對象與值進行二進制的或運算,一個爲真,就爲真
>>> a = 4
>>> b = 1
>>> a.__xor__(b)
>>> c = 0
>>> a.__xor__(c)
"""
pass
denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 分母 = 1 """
"""the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 虛數 """
"""the imaginary part of a complex number"""
numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 分子 = 數字大小 """
"""the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 實屬 """
"""the real part of a complex number"""
int2、布爾值
真或假
1 或 0
3、字符串
"Hello World!"
s = "nick"
#索引
print(s[0])
print(s[1])
print(s[2])
print(s[3])
#長度
ret = len(s)
print(ret)
#切片
print(s[1:3])
print(s.rsplit("ic"))
#替換
name = "Nick is good, Today is nice day."
a = name.replace("good","man")
print(a)
#連接兩個字符串
li = ["nick","serven"]
a = "".join(li)
b = "_".join(li)
print(a)
print(b)
#指定的分隔符將字符串進行分割
a = s.rpartition("i")
print(a)
#分割,前,中,後三部分
name = "Nick is good, Today is nice day."
a = name.partition("good")
print(a)
#for循環
for i in s:
print(i)
for i in range(5):
print(i)
# 反轉
s = 'ssssssssss111'
print(s[::-1]) # 111ssssssssss4、列表
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'taobao']
#在列表末尾添加新的對象
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T']
list.append('taobao')
print(list)
#將指定對象插入列表
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T','baidu']
list.insert(1,"Nick")
print(list)
#在列表末尾追加另一個序列中的多個值
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T','baidu']
list2 = ['nick','baidu']
list.extend(list2)
print(list)
#統計某個元素在列表中出現的次數
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T','baidu']
a = list.count('baidu')
print(a)
#從列表中找出某個值第一個匹配項的索引位置
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T','baidu']
a = list.index('baidu')
print(a)
#移除列表中的一個元素(默認最後一個元素)
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T','baidu']
list.pop()
print(list)
#移除列表中某個值的第一個匹配項
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T','baidu']
list.remove('baidu')
print(list)
#清空列表
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T']
list.clear()
print(list)
#刪除指定索引位置
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T','baidu']
del list[2]
print(list)
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T','baidu']
del list[1:3] -->顧頭不顧尾
print(list)
#複製列表
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T']
list2 = list.copy()
print(list2)
#對原列表進行排序
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T','baidu']
list.sort()
print(list)
#反向列表中元素
list = ['Google', 'baidu', 'T','baidu']
list.reverse()
print(list)5、元組(不可修改)
name = ('nick','jenney')#索引
name = ('nick','jenney')
a = name[0]
print(a)
#獲取指定元素的索引位置
name = ('nick','jenney')
a = name.index('nick')
print(a)
#切片
name = ('nick','jenney')
a = name[0:1]
print(a)
#計算元素出現的個數
name = ('nick','jenney')
a = name.count('nick')
print(a)
#長度
name = ('nick','jenney')
a = len(name)
print(a)
#for循環
name = ('nick','jenney')
for i in name:
print(i)6、字典(無序)
user_info = {
"name":"nick",
"age":18,
"job":"pythoner"
}
user_info = {
"name":"nick",
"age":18,
"job":"pythoner"
}
#根據key獲取值
a = user_info.get("age")
print(a)
a = user_info.get("Age",19")
print(a)
#所有的key 列表
a = user_info.keys()
print(a)
#所有的值,values
a = user_info.values()
print(a)
#所有項的列表形式
a = user_info.items()
print(a)
#獲取並在字典中移除
user_info.pop('age')
print(user_info)
#隨機並在字典中移除
user_info.popitem()
user_info.popitem()
print(user_info)
#清除內容
a = user_info.clear()
print(a)
#淺拷貝
a = user_info.copy()
print(a)
#如果key不存在,則創建,如果存在,則返回已存在的值且不修改
a = user_info.setdefault("age")
print(a)
user_info.setdefault("cool")
print(user_info)
#從序列鍵和值設置爲value來創建一個新的字典
a = dict.fromkeys(user_info)
print(("new dict: %s") % str(a))
#更新(兩個字典)
user_info = {
"name":"nick",
"age":18,
"job":"pythoner"
}
user_info2 = {
"wage":800000000,
"drem":"The knife girl"
}
user_info.update(user_info2)
print(user_info)7、set集合(無序、不重複)
s = set()
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}#添加元素
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
a.add('The knife girl')
print(a)
#更新
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
a.update(b)
print(a)
#a中存在。b中不存在,賦給新值
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
set = a.difference(b)
print(set)
#a中存在。b中不存在,並更新a
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
a.difference_update(b)
print(a)
#交集,賦給新值
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
set = a.intersection(b)
print(set)
#交集,更新a
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
a.intersection_update(b)
print(a)
#對稱交集
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
set = a.symmetric_difference(b)
print(set)
#對稱交集,更新a
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
a.symmetric_difference_update(b)
print(a)
#並集,賦給新值
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
set = a.union(b)
print(set)
#如果沒有交集,返回True,否則返回False
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny','The knife girl'}
set = a.isdisjoint(b)
print(set)
#是否是子序列
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny'}
set = a.issubset(b)
print(set)
#是否是父序列
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
b = {'nick','jenny'}
set = a.issuperset(b)
print(set)
#移除指定元素,不存在不報錯
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
a.discard('suo')
print(a)
#移除指定元素,不存在則報錯
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
a.remove('suo')
print(a)
a.remove('suo')
print(a)
#移除隨機元素,並賦給新值
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
set = a.pop()
print(set)
#清空
a = {'nick','jenny','suo'}
a.clear()
print(a)其他
1、for循環
用戶按照順序循環可迭代對象中的內容
name = ('nick','jenney')
for i in name:
print(i)2、enumrate
爲可迭代的對象添加序號
user_info = {
"name":"nick",
"age":18,
"job":"pythoner"
}
for k,v in enumerate(user_info,1):
print(k,v,user_info.get(v))3、range和xrange
指定範圍,生成指定的數字
range 前面小節已經說明了,range([start,] stop[, step]),根據start與stop指定的範圍以及step設定的步長,生成一個序列。
xrange 用法與 range 完全相同,所不同的是生成的不是一個list對象,而是一個生成器。
#python 2.7 版本 print range(1, 10) # 結果:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] print range(1, 10, 2) # 結果:[1, 3, 5, 7, 9] print range(30, 0, -2) # 結果:[30, 28, 26, 24, 22, 20, 18, 16, 14, 12, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2] #python 3.5 版本 a = range(10) print(a) #結果:range(0, 10)
>>> a = xrange(10) >>> print a xrange(10) >>> a = range(10) >>> a [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
for i in range(0, 100): print i for i in xrange(0, 100): print i
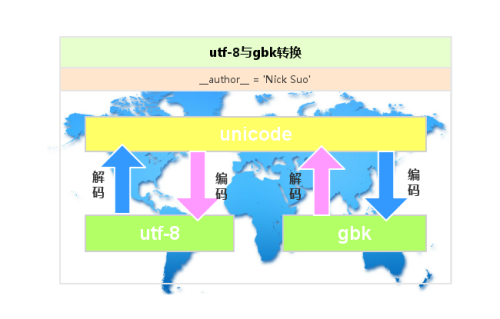
4、編碼與進制轉換
utf-8與gbk編碼轉換
把自己名字用進制表示出來
name = "翁孟鎧" a = bytes(name,encoding='utf-8') print(a) for i in a: print(i,bin(i)) #輸出結果(utf-8 三個字節表示一個漢字) b'\xe7\xb4\xa2\xe5\xae\x81' 231 0b11100111 180 0b10110100 162 0b10100010 229 0b11100101 174 0b10101110 129 0b10000001 b = bytes(name,encoding='gbk') print(b) for i in b: print(i,bin(i)) #輸出結果(gbk 兩個字節表示一個漢字) b'\xcb\xf7\xc4\xfe' 203 0b11001011 247 0b11110111 196 0b11000100 254 0b11111110